Our Research
Our research involves measuring low-temperature electronic, magnetic, and thermal properties of novel materials that manifest interesting physics and show potential for future electronic devices. These physical properties measurements, like electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and thermoelectric effects, involve attaching very fine wires to small crystalline specimens (mm sized), cooling them in liquid cryogens (liquid nitrogen and liquid helium), and using specialized voltmeters, current sources, and occasionally high-field magnets to study their properties. A parallel research effort involves making “thin films” of materials – thin coatings of 10-100 or so atomic layers of a material of interest deposited on a crystalline surface. The method of deposition involves the generation of a plasma (charged particles) from a target of selected material inside a high-vacuum chamber using a magnetron (sputtering) or a high-powered laser (pulsed-laser deposition). We study these films using x-ray crystallography (to determine their structural properties) and measure their low-temperature properties with the techniques mentioned above. Thin films are a first step toward making useful devices. Sometimes we are interested in studying interfaces between bulk crystalline materials and thin films deposited upon them.
Funding

Featured Articles
![]()
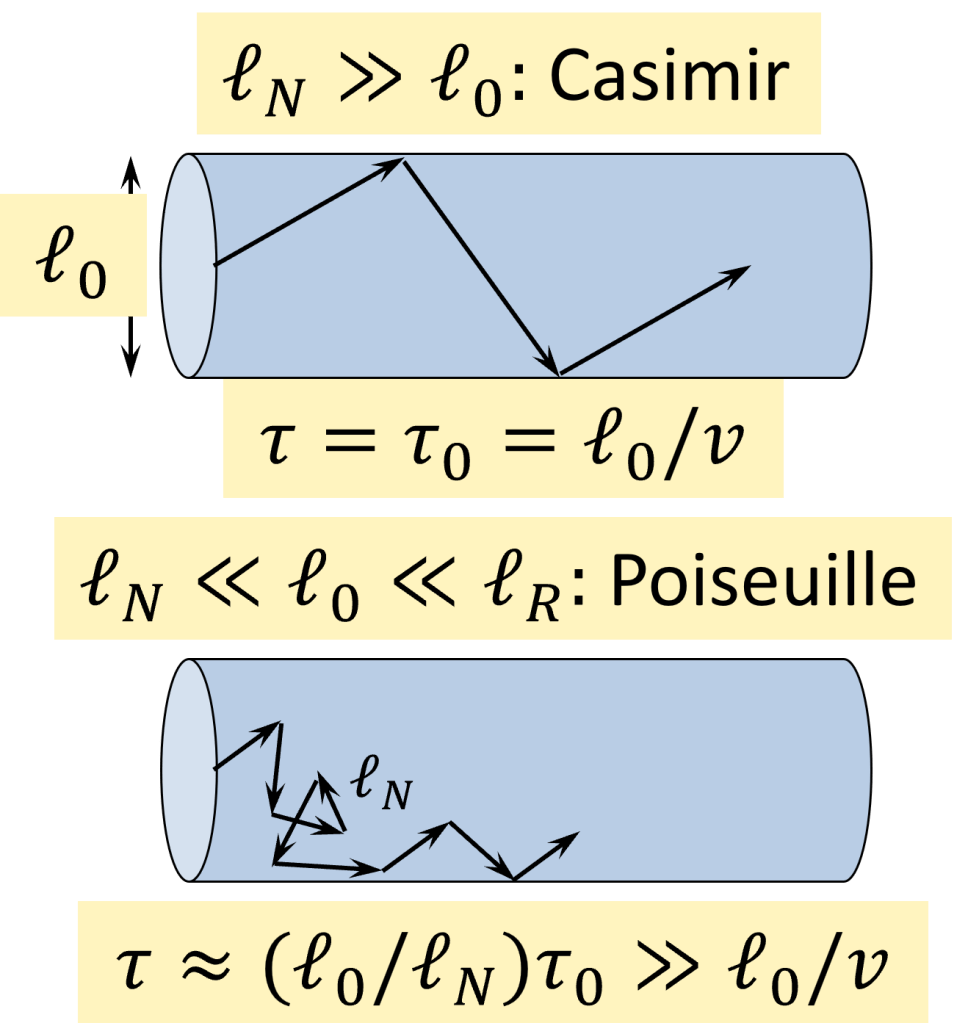
![]() Ballistic magnon heat conduction and possible Poiseuille flow in the helimagnetic insulator Cu2OSeO3. Prasai, Trump, Marcus, Akopyan, Huang, McQueen, and Cohn, Phys. Rev. B 95, 224407 (2017) (Editor’s Suggestion).
Ballistic magnon heat conduction and possible Poiseuille flow in the helimagnetic insulator Cu2OSeO3. Prasai, Trump, Marcus, Akopyan, Huang, McQueen, and Cohn, Phys. Rev. B 95, 224407 (2017) (Editor’s Suggestion).
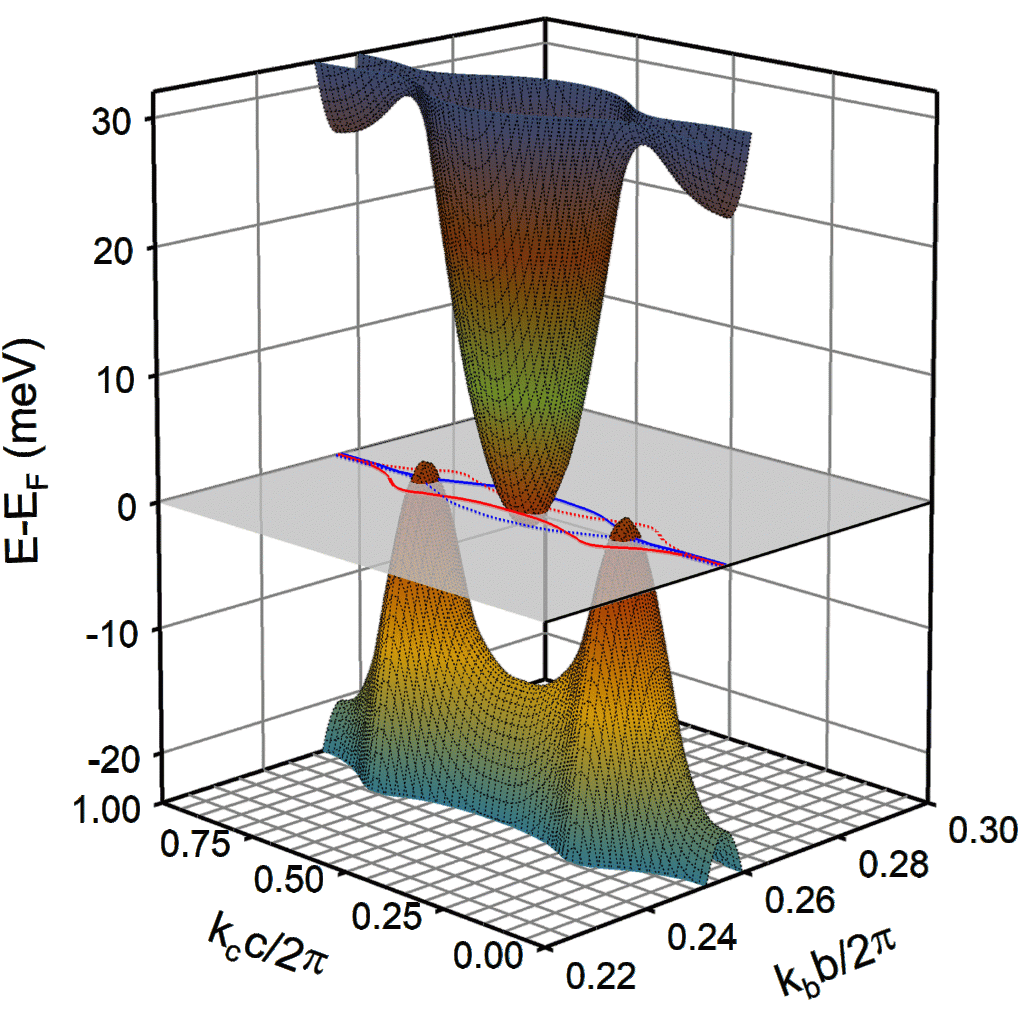
![]() Extreme Thermopower Anisotropy and Interchain Transport in the Quasi-One-Dimensional Metal Li0.9Mo6O17. Cohn, Moshfeghyeganeh, dos Santos, and Neumeier, Phys. Rev. Lett. 112, 186602 (2014).
Extreme Thermopower Anisotropy and Interchain Transport in the Quasi-One-Dimensional Metal Li0.9Mo6O17. Cohn, Moshfeghyeganeh, dos Santos, and Neumeier, Phys. Rev. Lett. 112, 186602 (2014).
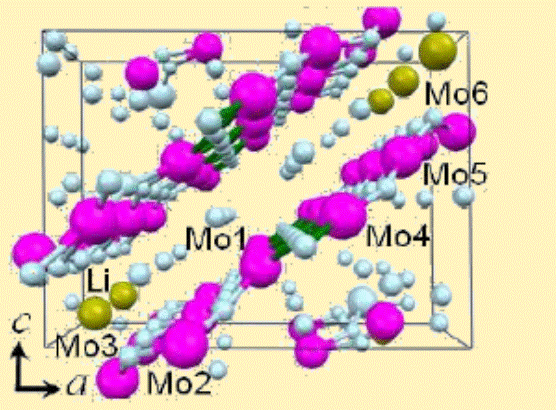
![]() Giant Nernst Effect and Bipolarity in the Quasi-One-Dimensional Metal, Li0.9Mo6O17. Cohn, White, dos Santos, and Neumeier, Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, 056604 (2012) (Editor’s Suggestion) Featured in Physics Synopsis.
Giant Nernst Effect and Bipolarity in the Quasi-One-Dimensional Metal, Li0.9Mo6O17. Cohn, White, dos Santos, and Neumeier, Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, 056604 (2012) (Editor’s Suggestion) Featured in Physics Synopsis.
![]() Giant Electrothermal Conductivity and Spin-phonon Coupling in an Antiferromagnetic Oxide. Chiorescu, Neumeier, and Cohn, Phys. Rev. Lett. 101, 257202 (2008).
Giant Electrothermal Conductivity and Spin-phonon Coupling in an Antiferromagnetic Oxide. Chiorescu, Neumeier, and Cohn, Phys. Rev. Lett. 101, 257202 (2008).
![]() Impurity conduction and magnetic polarons in antiferromagnetic oxides. Chiorescu, Cohn, and Neumeier. Phys. Rev. B 76 020404(R) (2007).
Impurity conduction and magnetic polarons in antiferromagnetic oxides. Chiorescu, Cohn, and Neumeier. Phys. Rev. B 76 020404(R) (2007).
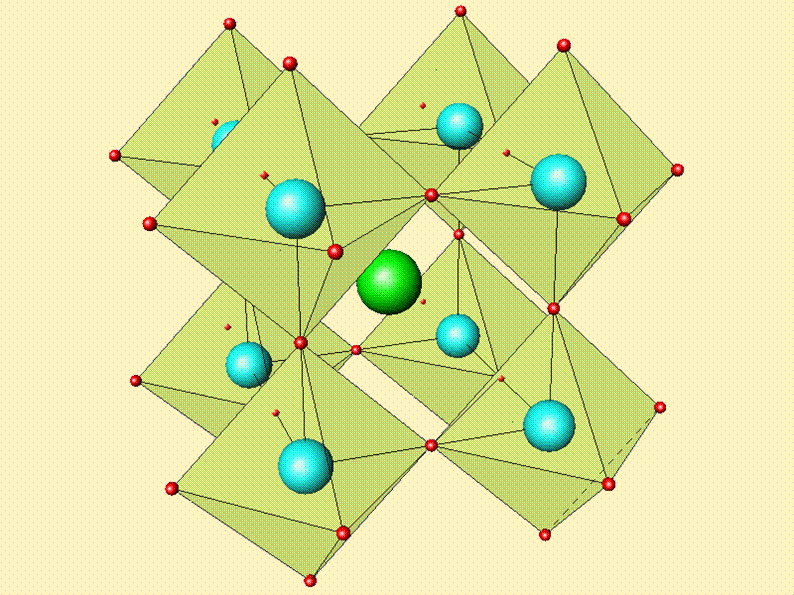
![]() Polaron transport in the paramagnetic phase of electron-doped manganites. Cohn, Chiorescu, and Neumeier. Phys. Rev. B 72 024422 (2005).
Polaron transport in the paramagnetic phase of electron-doped manganites. Cohn, Chiorescu, and Neumeier. Phys. Rev. B 72 024422 (2005).
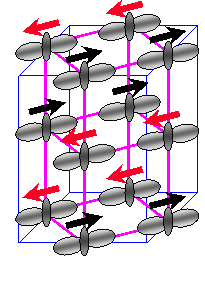
![]() Low-temperature permittivity of insulating perovskite manganites. Cohn, Peterca, and Neumeier. Phys. Rev. B 70 214433 (2004).
Low-temperature permittivity of insulating perovskite manganites. Cohn, Peterca, and Neumeier. Phys. Rev. B 70 214433 (2004).
![]() Heat conduction and magnetic phase behavior in electron-doped Ca1-xLaxMnO3 (0< x <0.2). Cohn and Neumeier. Phys. Rev. B 66, 100404 (2002).
Heat conduction and magnetic phase behavior in electron-doped Ca1-xLaxMnO3 (0< x <0.2). Cohn and Neumeier. Phys. Rev. B 66, 100404 (2002).
![]() Possible signatures of magnetic phase segregation in electron-doped antiferromagnetic CaMnO3. Neumeier and Cohn. Phys. Rev. B 61, 14319 (2000).
Possible signatures of magnetic phase segregation in electron-doped antiferromagnetic CaMnO3. Neumeier and Cohn. Phys. Rev. B 61, 14319 (2000).
![]() Hole localization in underdoped superconducting cuprates near 1/8 doping. Cohn, Popoviciu, Lin, and Chu. Phys. Rev. B 59, 3823 (1999).
Hole localization in underdoped superconducting cuprates near 1/8 doping. Cohn, Popoviciu, Lin, and Chu. Phys. Rev. B 59, 3823 (1999).

![]() Glasslike Heat Conduction in High-Mobility Crystalline Semiconductors. Cohn, Nolas, Fessatidis, Metcalf, and Slack. Phys. Rev. Lett. 82, 779 (1999).
Glasslike Heat Conduction in High-Mobility Crystalline Semiconductors. Cohn, Nolas, Fessatidis, Metcalf, and Slack. Phys. Rev. Lett. 82, 779 (1999).